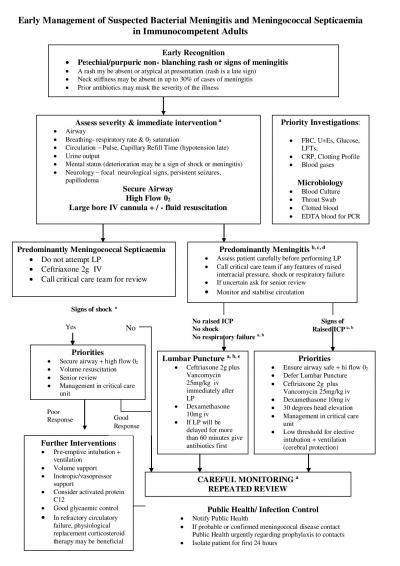
a Warning Signs
The following warn of impending worsening shock, respiratory failure or raised intracranial pressure and require urgent senior review and intervention
(See algorithm)
- Rapidly progressive rash
- Poor peripheral perfusion CRT > 4secs, oliguria and systolic BP < 90
(hypotension often a late stage)
- RR < 8 or > 30
- Pulse Rate < 40 or > 140
- Acidosis; ph < 7.3 or BE < –5
- WBC < 4
- Marked depressed conscious level (GCS < 12) or a fluctuating conscious level (fall in GCS >2)
- Focal neurology
- Persistent seizures
- Bardycardia and hypertension
- Papillodema
b CT Scan and Meningitis
- This investigation should only be used when appropriate:
- A normal CT scan does not exclude raised intracranial pressure.
- If there are no clinical contraindications to LP a CT scan is not necessary beforehand.
- Subsequently a CT scan may be useful in identifying dural defects predisposing to meningitis.
c Appropriate antibiotics for bacterial meningitis
- Review with microbiology.
- Amoxicillin 2g IV 4 hrly should be added for individual > 50 yrs to cover listeria (co-trimoxazole 10mg/kg IV if penicillin hypersensitive)
- Amend antibiotics on the basis of microbiology results.
- Uncertain Hx of allergy (i.e. more than rash) or severe allergy. Chloramphenicol 25mg/kg IV and discuss with microbiology dept.
d Corticosteroids in adult meningitis
- Dexamethasone 0.15 mg/kg IV started with or just before the first dose of antibiotics, particularly where pneumoccal meningitis is suspected.
- Do not give unless you are confident you are using the correct antimicrobials.
- Stop the dexamethasone if non-bacterial cause is identified.
e Lumbar puncture
If there will be delay before lumbar punctures start antibiotics immediately once blood cultures have been taken and prior to lumbar puncture.
Encephalitis Acyclovir 10mg/kg
* http://www.meningitis.org/health-professionals/hospital-protocols-adults