The first and most important aspect of tetanus prevention is good and adequate surgical toilet for all wounds.
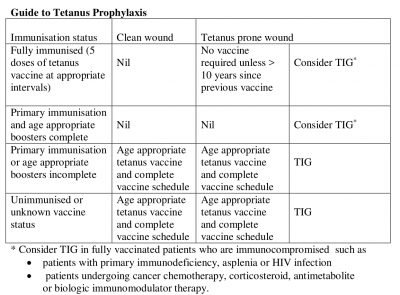
If a patient has had a total of 3 doses of tetanus vaccine at the appropriate intervals, they are considered to have immunity for 10 years.
Tetanus vaccine given at the time of a tetanus prone injury may not boost immunity early enough to give additional protection within the incubation period of tetanus. This means that following a tetanus prone wound, where the individual has received a full 3 dose course of tetanus vaccine at the recommended intervals, no further doses of vaccine are recommended. If the risk of tetanus is especially high e.g. the wound is contaminated with stable manure, then tetanus immunoglobulin (TIG) should be given to give immediate additional protection.
For those people whose immunisation schedule is not up to date or whose status is unknown, a booster dose of tetanus toxoid should be given at the time of treatment of an injury and further doses given, as required, to complete the recommended 3 dose schedule. In this situation tetanus immunoglobulin (TIG) should be given for any injury defined as a tetanus prone wound.
Tetanus prone wounds
The following wounds are considered tetanus-prone:
- wounds or burns that require surgical intervention that is delayed for more than six hours
- wounds or burns that show a significant degree of devitalised tissue or a puncture type injury, particularly where there has been contact with soil or manure
- wounds containing foreign bodies
- compound fractures
wounds or burns in patients who have systemic sepsis.
Tetanus Immunoglobulin (TIG)
Indications
- Tetanus prone wounds in patients who have not received at least three doses of tetanus toxoid in the previous ten years (see table over leaf).
- Patients with impaired immunity, who suffer a tetanus prone wound, may not respond to anti tetanus toxoid and should be given tetanus immunoglobulin (TIG) irrespective if their immunisation status.
Dose and route of administration
250 IU intramuscularly into the anterolateral thigh.
The single dose is doubled to 500 IU (2 ml) when:
- The injury occurred more than 24 hours previously
- The patient weighs more than 90 kg
- The wound is heavily contaminated
- The wound is infected or involves a fracture.
Tetanus Immunoglobulin.
Td
Tetanus, low-dose diphtheria
Td/IPV
Tetanus, low-dose diphtheria/ Inactivated Polio Virus vaccine
Currently the vaccines available are Td and Td/IPV (Revaxis).